Breast Augmentation
- Home
- Breast Augmentation
What is Breast Augmentation?
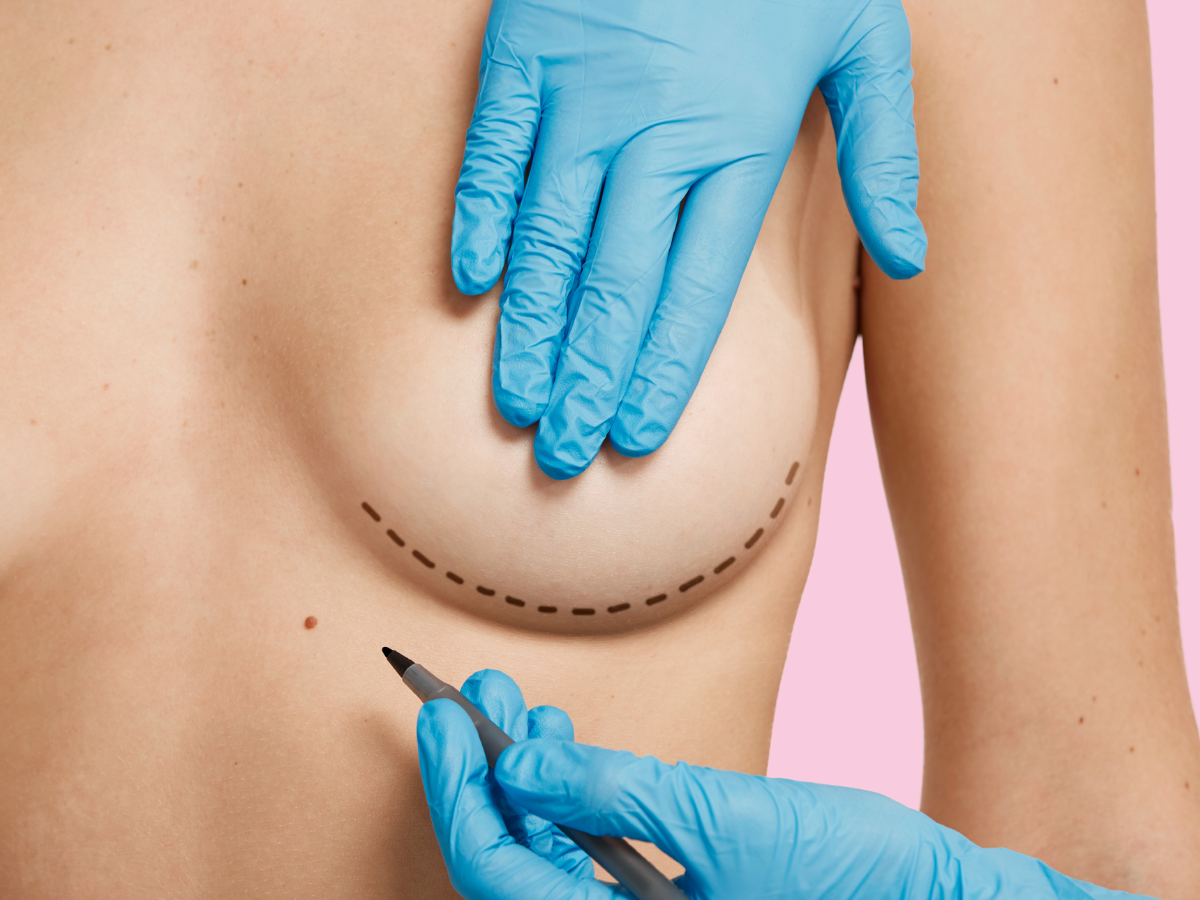
Breast augmentation is a cosmetic surgical procedure designed to enhance the size, shape, or fullness of the breasts. It is commonly performed by inserting breast implants (silicone or saline) or through fat transfer from other areas of the body. This procedure is sought by individuals looking to improve the appearance of their breasts due to personal aesthetic reasons, post-pregnancy changes, or reconstruction after breast surgery (such as mastectomy).
Concerns Related to Breast Augmentation:
- As with any surgery, there are risks of complications such as infection, bleeding, or adverse reactions to anesthesia.
- Implants may rupture, leak, or develop complications like capsular contracture, where scar tissue forms around the implant and causes discomfort or a distorted appearance.
- Breast implants are not lifetime devices and may need replacement after 10 to 15 years, leading to additional surgeries.
- Some people may experience changes in nipple or breast sensation after surgery, which could be temporary or permanent.
Benefits of Breast Augmentation:
- Breast augmentation can improve the size, shape, and symmetry of the breasts, helping individuals achieve their desired look and proportions.
- Breast augmentation can restore breast volume that may have been lost after pregnancy, breastfeeding, or significant weight loss.
- For individuals who have undergone mastectomy or breast reconstruction surgery, breast augmentation can help restore the natural shape and appearance of the breasts.
- The procedure is highly customizable, allowing individuals to choose their desired implant size, shape, and type to match their aesthetic preferences.
Augmentation Treatment
Before & After

FAQ's
Here, we’ve answered some common questions to help you understand more about Breast augmentation , the procedure, recovery, and what to expect. If you have any further queries, feel free to reach out to us for more information.
The two main types of breast implants are silicone and saline. Silicone implants are filled with a gel, while saline implants are filled with sterile salt water.
Initial recovery usually takes 1 to 2 weeks, with most people returning to work and light activities during this time. Full recovery, including the resumption of strenuous activities, may take 4 to 6 weeks.
Breast implants are generally considered safe when performed by a qualified plastic surgeon. However, there are risks associated with any surgery, including infection, implant rupture, and capsular contracture (scar tissue around the implant).
Many women can still breastfeed after breast augmentation, but the ability to breastfeed may depend on the type of surgery and implant placement. Discuss your future breastfeeding plans with your surgeon before the procedure.
Breast implants can make it more challenging to perform mammograms. You should inform your radiologist about your implants so that they can adjust the imaging technique to ensure a thorough breast exam.
